Overtime-Weighted Average WAOT NC DOL
Book a Sage HCM demo today and discover the power of a payroll software that’s designed for your business. For more information on how to classify employees for overtime, check with the Department of Labor or a lawyer experienced in employment law. Form 940, which reports federal unemployment tax (FUTA), must also be filed annually. You should check if FUTA was only applied to the first $7,000 of wages per employee. Before issuing W-2s, you should review payroll totals https://www.federicomottavideo.it/cost-of-goods-manufactured-how-to-calculate-cogm/ to ensure they match quarterly payroll tax filings.

Corporate tax

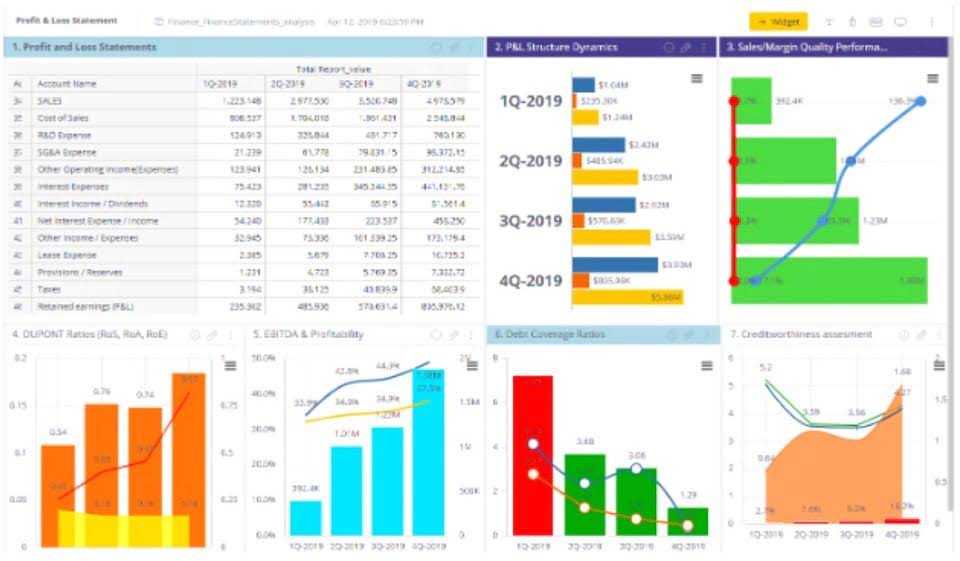
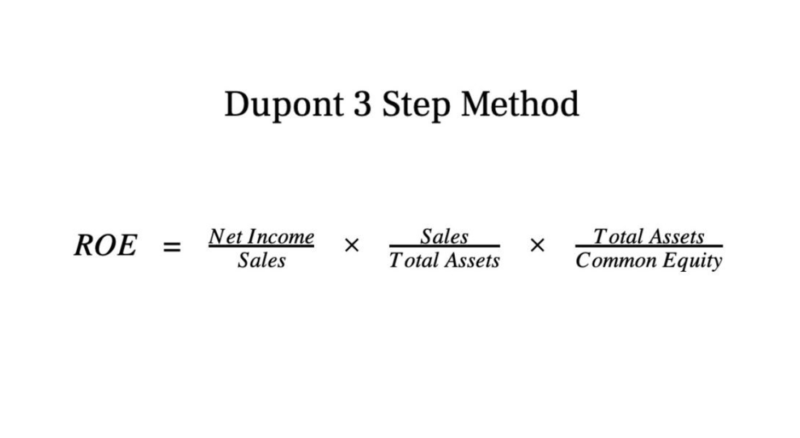
The primary purpose of the Weighted Average Overtime Calculator is to combine multiple overtime rates into a single average rate that accurately reflects the proportionate amount of work done at each pay rate. This helps in calculating overtime pay when multiple rates are involved due to varying work conditions or agreements. California is a prime weighted overtime example of a state with more stringent overtime rules. Employers must contend with daily overtime, weekly overtime, and double-time pay. When a California employee works at multiple rates, the “regular rate of pay” is still the weighted average for the entire workweek, which is then used as the base for the state’s various multipliers. Calculating overtime is an essential function of any payroll or HR team.
Practical Calculation Examples: Streamline Your Payroll Process
- Many employers mistakenly believe it’s simply an employee’s standard hourly wage.
- Our software also makes it easy to manage other aspects of your business, giving you everything you need for effective workforce and labor management.
- ADP does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, reliability, and completeness of the content.
- Missing or incorrect paperwork can lead to underwithholding, overwithholding, delayed pay, or compliance issues later.
- WAOT can also be used when the employee has overtime hours and is partially compensated by non-hour based payments like commissions.
- These forms directly affect how payroll calculates withholdings and issues pay.
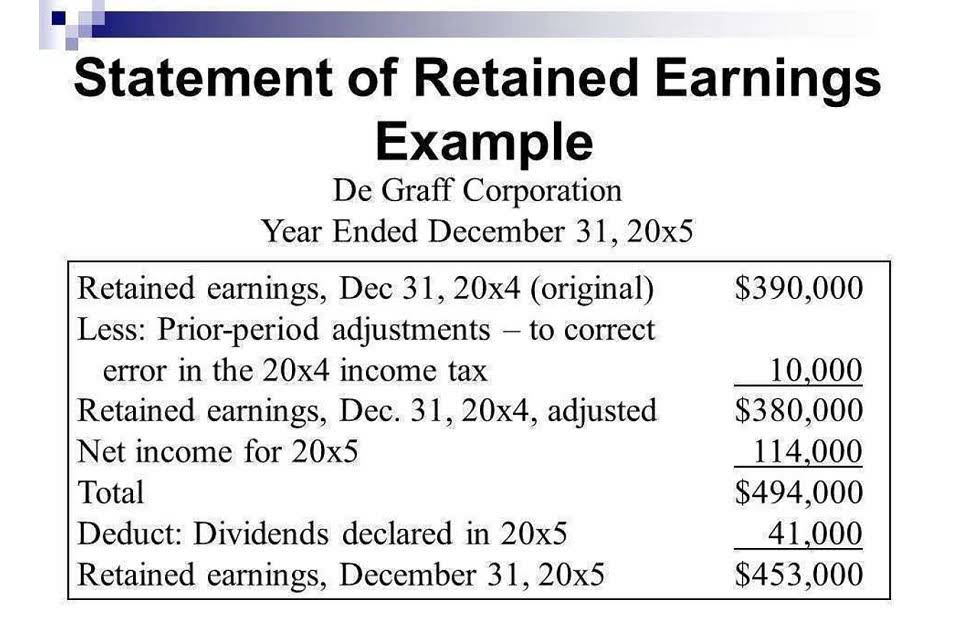
The Total Earnings amount in Part 1 is then divided by the Total Hours Worked (both Regular and Overtime) to determine the Weighted Hourly Rate. Embracing these principles sets a strong foundation for all your future payroll endeavors. Having explored how our free calculator and template streamline basic compliance, it’s now crucial to delve into the more intricate scenarios where precision is paramount. The contents of this document do not have the force and effect of law and are not meant to bind the public in any way.
How TurboTax supports year-end payroll filing
The overtime pay requirement cannot be met through the use of compensatory time off (comp time) except under special circumstances applicable only to state and local government employees. The One Big Beautiful Bill “no tax on overtime” provision creates a new federal income tax deduction for qualified overtime compensation. Under this provision, employees may deduct their overtime premium, specifically the portion of overtime pay that exceeds their regular rate. You need a reliable way to capture all hours worked, including opening prep, closing duties, and split shifts. If employees work different roles at different pay rates, those hours must be tracked separately so payroll can apply the correct rate and calculate overtime properly.
- You use it when your non-exempt employee makes more than one pay rate and works overtime in a workweek.
- In situations in which an employee is covered by both Federal and state wage laws, the employee is entitled to the greater benefit or more generous rights provided under the different parts of each law.
- Payroll teams maintain this year-end QOC total, and employees use it to estimate or claim their overtime deduction.
- Blended overtime is calculated just like regular overtime, but with an extra consideration.
- Watch for inconsistencies between sales and reported tips, as these can signal reporting issues that create tax problems later.
- It requires employers to average all regular rates of pay for a given workweek before applying the overtime premium.
Excluding pay items from WAOT calculations
A workday in California is defined as any 24-hour period starting at the same time each calendar day. Employers can set different workdays for different shifts, but changes must not aim to circumvent overtime obligations. Consider an employee who earns $550 in commissions over 35 hours, with 5 of those hours being overtime. Consider an hourly employee with a wage of $20 per hour working a 10-hour day. The final step of the calculation is adding the Total Earnings from Part 1 to the https://www.bookstime.com/ Overtime Premium Pay of Part 4 which is ultimately applied to the employee’s gross pay. This is the extra amount the employee earns for each hour of overtime worked.
Are there Industry-Specific Overtime Rules in California?

The weighted average approach ensures that all earnings contribute proportionally to the overtime base. Weighted overtime calculations are essential for ensuring fair compensation and compliance with labor laws. Employers need to make sure they are compensating their employees appropriately, especially when dealing with overtime that requires different multipliers, such as holiday or weekend work. Calculating overtime for employees who perform multiple jobs with varying pay rates can be complex.





